The Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard is a rich, visual language for describing even the most complex business processes.
- BPMN makes our understanding of a process explicit.
- It’s easy for people to understand
- It’s sufficiently rigorous to aid in the design of supporting information technologies.
Like any language, BPMN has a vocabulary.
- Vocabulary elements are visualized using symbols.
- The language has a syntax. That is, there are rules regarding how vocabulary elements can be combined.
- Each vocabulary element has a precise meaning.
BPMN contains an expansive symbolic vocabulary.
The BPMN symbolic language
However, just four elements are enough to get started: activities, events, gateways, and sequence flows:

The basic BPMN symbols
- Activities represent actions to be taken and tasks to be completed.
- Events indicate the conditions that trigger and complete an instance of a process.
- Gateways manage the splitting and merging of a process flow.
- The sequence flow indicates how a process progresses from start to end.
For example, consider a recruitment process for an executive peer exchange. Here’s how the basic process might be described using the basic BPMN elements:
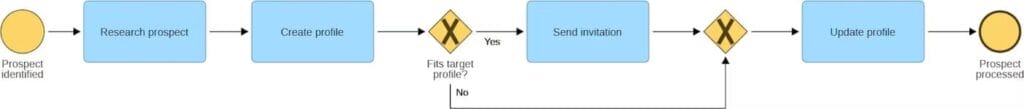
A process model using basic BPMN symbols
- The process starts when a prospect has been identified.
- The background of the prospect is researched.
- Next, a profile is created and added to a CRM database.
- If the prospect fits the target profile, an invitation is sent, the prospect’s profile is updated, and the process ends.
- Alternatively, if the prospect doesn’t fit the target profile, her profile is updated accordingly, and the process ends.
For Discussion
- What start and end event(s) are associated with your business process?
- What activities comprise the process, and in what order are they to be completed?
- What contingencies might need to be reflected with a gateway?

